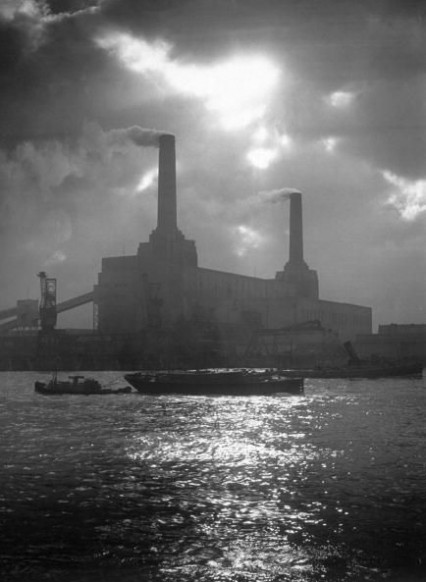
It has occasionally been said that the rather sad and disgracefully neglected Battersea Power Station in South London looks a bit like a billiard table turned upside down. It’s not a particularly good discription – the proportions aren’t right at all. Although if it was a billiard table and the right way up and it was before 1953, it would have fallen over because it only had two legs.
Battersea Power Station as we know it today, with its familiar four chimney layout, was actually two individual power stations – Battersea ‘A’ and Battersea ‘B’ but constructed eventually in the form of a single building with the last of the iconic fluted concrete chimneys only being raised as late as 1955.
Most of the extraordinary detail of the power station, that once made the London writer Felix Barker to compare Battersea to the great church of Sainte-Cécile at Albi in the south of France, has now gone – obliterated, by over twenty-five years of seemingly complete indifference to one of London’s famous landmarks by the various property development companies who have sold it on rather than developing it.
During the 1920s electricity was supplied to London by small companies that were often dedicated to single industries or groups of factories. Any excess power was then sold to the public. However due to differing standards of voltage and frequency that were being provided, parliament in 1925, decided that the power grid should be a single system.
Several private power companies pre-empted the feared nationalisation (which wasn’t to arrive until after the war in 1948 with the British Electricity Authority) by forming the London Power Company which planned several very large stations for London. The first of these they came up with was in the Battersea area between the Thames and the Nine Elms Lane.
In 1928, with the architect Theo J Halliday in charge, construction started on the power station despite furious opposition by public figures such as the Archbishop of Canterbury. To appease the public, who were worried about the general size of the building and the pollution it might cause, the London Power Company hired the famous architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott of Liverpool Cathedral and the red telephone box fame. He was known to the press as ‘architect of the exterior’ and it was his idea to turn the previously planned square chimneys into the fluted classical columns we know today.
Work started on Battersea ‘B’ Station soon after the war, still under the auspices of the London Power Company. However by the time it completed building opened the UK’s electric supply industry had been nationalised into the hands of initially the British Electricity Authority which subsequently became, in 1955, the Central Electricity Generating Board and then finally (I think) the Central Electricity Generating Board in 1957.

The building of Battersea 'B' in 1951. 'One day, we will all have to wear day-glo high-vis jackets and hard-hats even when we're walking on the ground'.
In 1964 Battersea Power Station had a bad fire that caused power failures throughout London. Unfortunately it was due to be the opening night of BBC2 which in the end had to be delayed until the following day at 11am.
Incidentally Battersea Power Station is often described as Europe’s largest brick building but a quick Google describes two other buildings also as’Europe’s largest brick building’ – namely The Britannia Grand Hotel in Scarborough and the Malbark Castle in Poland.
The aforementioned Church of Sainte-Cecile in Albi, however, is often described as the world’s largest brick building, and as France is in Europe, that’s the building I’m going for. Churches though, are meant to look great. Power Stations, whether they have two or four chimneys, generally, aren’t.
The Jam – News Of The World
Pink Floyd – video to Pigs On The Wing which include fantastic views of Battersea Power Station
Rowan Atkinson’s spoof of BBC2′s opening night